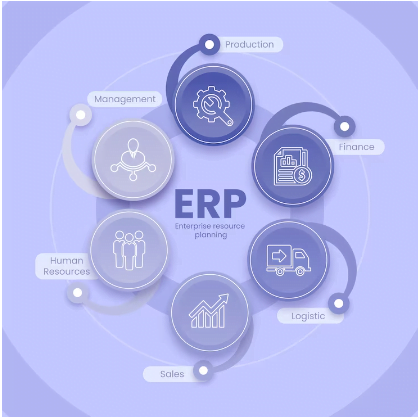
ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning. ERP software is a comprehensive business management system that integrates various core processes and functions within an organization. It enables the efficient and centralized management of resources, data, and operations across different departments, including finance, human resources, manufacturing, supply chain, customer relationship management, and more.
The key Objective Of ERP software is to provide a unified and real-time view of business processes and data, enabling organizations to streamline operations, enhance collaboration, and make informed decisions.
Integration of Business Functions:
ERP software integrates various departments and functions within an organization, consolidating data from different sources into a single database. This allows for seamless communication and sharing of information across departments, eliminating data silos and improving overall efficiency.
Centralized Data Management:
ERP software serves as a centralized repository for all relevant business data. It allows for the storage, management, and retrieval of data related to customers, suppliers, inventory, sales, financials, and more. This centralized data management ensures data accuracy, consistency, and accessibility across the organization.
Process Automation:
ERP systems automate repetitive and manual tasks by streamlining and standardizing business processes. It reduces the need for manual data entry, enables workflow automation, and provides tools for process optimization, resulting in increased efficiency, reduced errors, and improved productivity.
Improved Decision-Making:
ERP software provides real-time insights and reporting capabilities, enabling organizations to make data-driven decisions. It offers comprehensive dashboards, analytics, and reporting tools that allow users to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs), track business metrics, and analyze trends. This empowers management with accurate information for strategic planning and decision-making.
Supply Chain Management:
ERP software facilitates effective supply chain management by integrating procurement, inventory management, and order fulfillment processes. It helps organizations optimize inventory levels, track materials and products throughout the supply chain, manage vendor relationships, and streamline procurement processes.
Financial Management:
ERP systems include modules for financial management, such as general ledger, accounts receivable, accounts payable, budgeting, and financial reporting. This enables organizations to manage financial transactions, track expenses, generate financial statements, and comply with accounting standards.
Scalability and Flexibility:
ERP software is designed to accommodate the growth and changing needs of businesses. It can scale as the organization expands, support multiple locations, and adapt to evolving industry requirements. Additionally, ERP systems often offer customization options to tailor the software to specific business processes and workflows.
Implementing an ERP system requires careful planning, training, and data migration, as it often involves significant changes to existing processes and systems. However, the benefits of ERP software include improved operational efficiency, enhanced collaboration, better resource utilization, and increased visibility into business performance.
